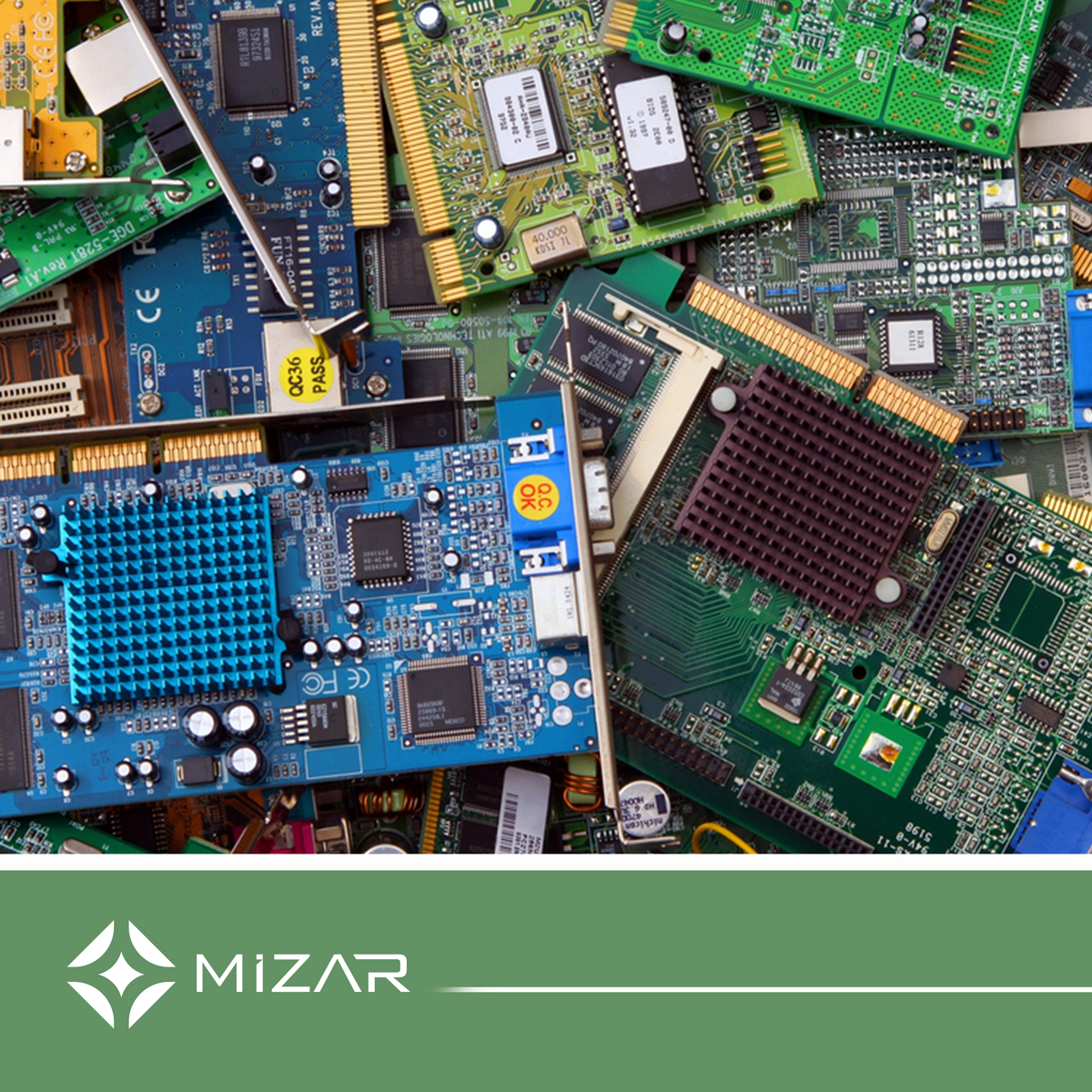
Recycling Technologies for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) represent one of the most complex and critical areas in the recycling industry. Due to the valuable metals and rare elements they contain, PCBs play a significant role in the recycling of electronic waste. Precious metals such as copper, gold, silver, and palladium are the main components targeted in PCB recovery. However, this recovery process requires careful technology due to the complexity of the structure of the circuit boards.
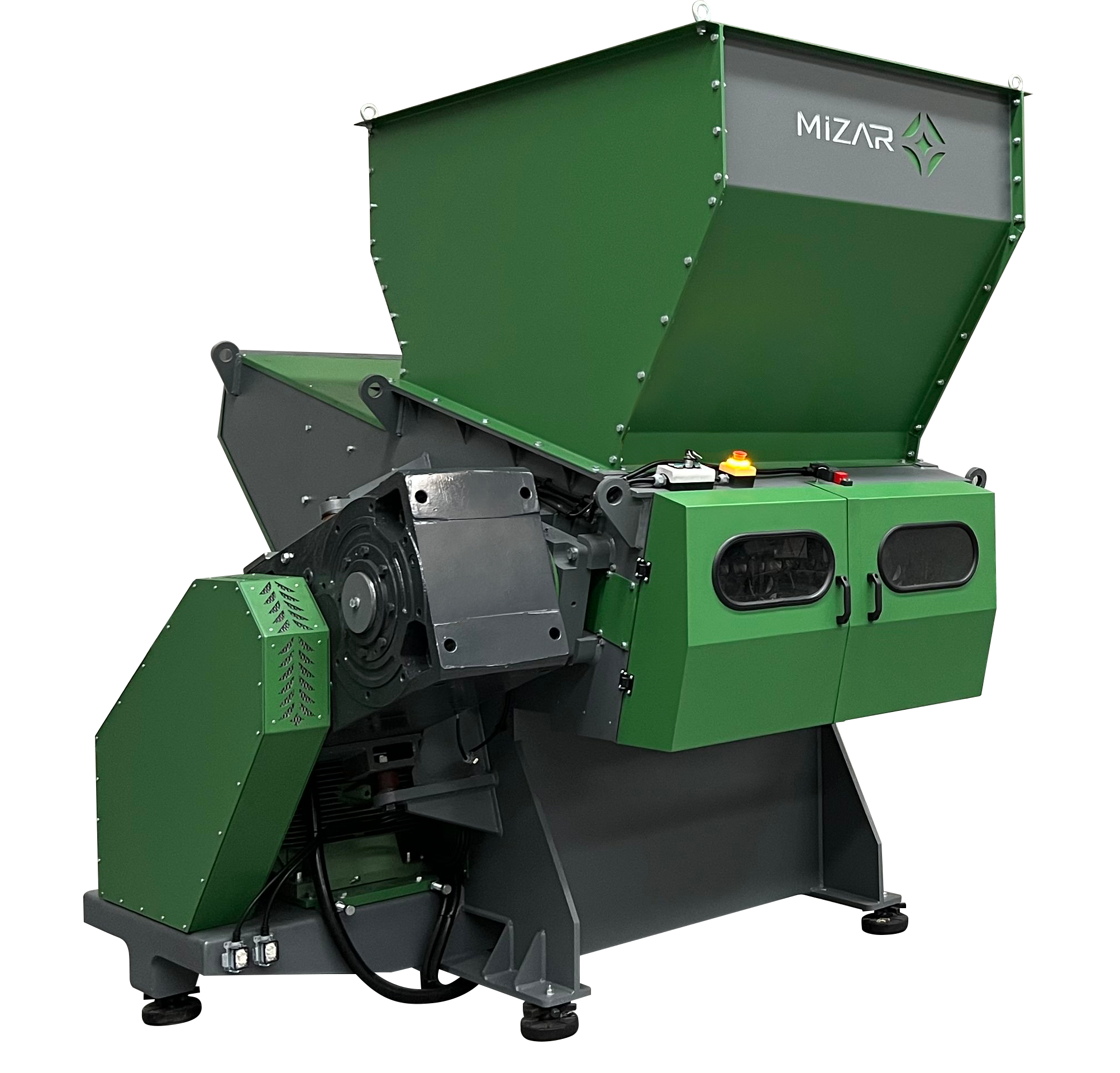
Mizar's PCB recycling machines are specifically designed to tackle this challenging process. The recycling process typically begins with a pre-processing stage. Circuit boards are shredded using double-shaft shredders, reducing larger components to ideal sizes for subsequent operations. This initial stage effectively separates the multi-layered structure of circuit boards and facilitates the exposure of valuable metals.
The shredded circuit boards are then directed to granulators. The granulation process aims to achieve finer and more homogeneous particles. During this process, Mizar's machines operate with high precision, ensuring the separation of valuable metals from plastics and other foreign materials. Advanced equipment such as magnetic separators and densimetric separators are utilized to enhance metal purity and maximize recovery rates.
One of the most critical stages of PCB recycling is minimizing environmental impacts. Some substances found in circuit boards contain chemical compounds that can be harmful to the environment. Mizar's recycling machines are designed to safely separate these hazardous materials. These machines provide a safe operation for both workers and the environment, forming the basis of sustainable recycling processes.
In conclusion, Mizar's PCB recycling machines offer the best solutions in terms of high efficiency, valuable metal recovery, and environmental sustainability. The recovery of PCBs is a critical step for the proper management of electronic waste and for minimizing the harm to nature.